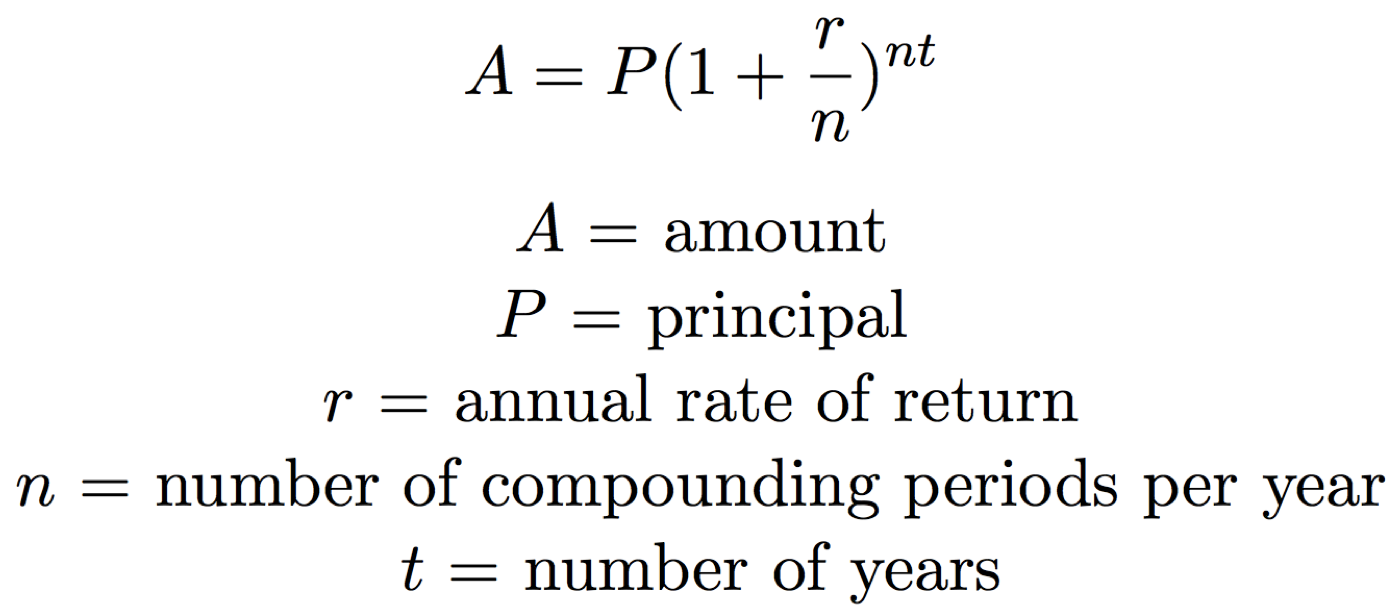
This means that [latex]0.7\%[/latex] per month is equal to [latex]8.4\%[/latex] compounded monthly. Calculate the nominal interest rate for the following periodic interest rates. Calculate the periodic interest rate for the following nominal interest rates.
How to Calculate Compound Interest
The Compound Interest Calculator below can be used to compare or convert the interest rates of different compounding periods. Please use our Interest Calculator to do actual calculations on compound interest. $10,000 invested at a fixed 5% yearly interest rate, compounded yearly, will grow to $26,532.98 after 20 years. This means total interest of $16,532.98 anda return on investment of 165%. To illustrate the effect of compounding, let’s take a look at an example chart of an initial $1,000 investment.

Interactive compound interest formula
I created the calculator below to show you the formula and resulting accrued investment/loan value (A) for the figures that you enter. If you’re using Excel, Google Sheets or Numbers, you can copy and paste the following into your spreadsheet and adjust your figures for the first fourrows as you see fit. This example shows monthly compounding (12 compounds per year) with a 5% interest rate. In the following sections, we’ll explore variations of the formula for annual, quarterly, monthly and daily compounding. We’ll also provide a more detailed step-by-step explanation ofhow to use the formula and discuss how to it within an Excel spreadsheet. The calculations results given by the compound interest calculator serve only as guide for potential future value.
Everyday Calculation
Therefore, compound interest can financially reward lenders generously over time. The longer the interest compounds for any investment, the greater the growth. Continuous compound interest is when interest is earned continuously, at the smallest possible interval, leading to the highest form of growth for an investment or loan. Compound interest works by a loan or investment earning interest on the initial value plus the prior interest earned. This means that you earn interest on prior interest, leading to exponential growth for an investment.
What are the most common compounding periods?
Use the information provided by the software critically and at your own risk. Compound interest is a type of interest in which the interest amount is periodically added to the principal amount and new interest is subsequently accrued over interest from past periods. It is a very powerful tool for increasing your capital and is a basic calculation related to personal savings plan or strategy, as well as long term growth of a mutual fund or a stock market portfolio. Compounding interest is the most basic example of capital reinvestment.
Again, we calculate twelve different future values, and we sum those future values to get the value in the account at the end of three years. That amount is compounded quarterly for the number of quarters remaining before the end of the three-year period. Think of this as twelve different compound interest calculations, one for each quarter that you deposit $135. At the end of three years, simply add up each compound interest calculation to get your total future value. The present value is simply the amount of money that will be invested, i is the interest rate for each time interval, and n is the number of compounding intervals. The formula can be used when compounding annually, monthly, or at whatever time interval over which you wish to compound.
Enter the present value, additional contributions (if any), interest rate, and length of time in years below. Compound interest means that the interest you earn in each compounding period is added to your principal, so that the balance doesn’t merely grow, it grows at an increasing rate. Calculate the compounding frequency for the following nominal and periodic interest rates. The nominal interest rate ([latex]j[/latex]) is the quoted or stated interest rate annually.
- This interest is added to the principal, and the sum becomes Derek’s required repayment to the bank one year later.
- However, it is important to understand the effects of changing just one variable.
- Now that you understand how powerful compound interest can be, let’s break down how it’s calculated.
- Calculate the nominal interest rate for the following periodic interest rates.
Due to the way the compound interest formula works, the more frequently you compound, the more interest earned (or charged). Use a daily compound interest calculator to better determine your day-to-day rates. Let’s say you invest $1,000 in an account that pays 4% interest compounded annually.
Using a tool like the compound interest calculator will provide the quickest and easiest way to calculate compound interest. This calculator uses the compound interest formula to find the total principal plus accrued interest. It uses this same formula to solve for principal, rate or time given the other known values. You can also use the compound interest equation to set up a compound interest calculator in an Excel1 spreadsheet. Compound interest is different from simple interest where the interest amount is calculated at the beginning of the investment or loan.
But for real and accurate numbers, it is possible to input figures in order to account for inflation. Then to figure out the interest earnings you would subtract the original principal from the the difference between fixed and variable costs result. Now that we’ve looked at how to use the formula for calculations in Excel, let’s go through a step-by-step example to demonstrate how to make a manualcalculation using the formula…
